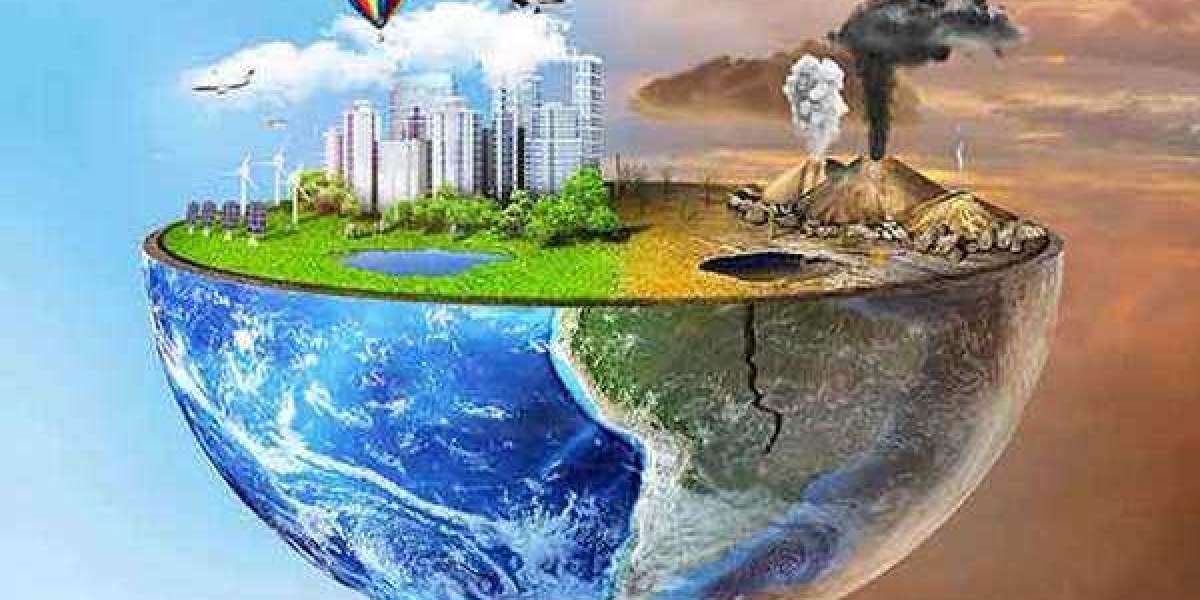
Climate change refers to the long-term alteration in Earth's climate patterns, primarily due to human activities such as burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. The impacts of climate change are already being felt around the world, and they are expected to become more severe in the coming years. One of the most significant impacts of climate change is its effect on nature, which includes everything from ecosystems to plant and animal species.
One of the primary ways in which climate change affects nature is through changes in temperature and weather patterns. Rising temperatures can cause changes in the timing and location of seasonal events, such as migration, hibernation, and flowering, leading to disruptions in the life cycles of plants and animals. This, in turn, can lead to mismatches between species that depend on each other for food and pollination. For example, if a plant blooms earlier than usual due to warmer temperatures, but the insect that pollinates it has not yet emerged, this can affect the survival of both the plant and the insect.
In addition to changes in temperature, climate change also affects weather patterns. This can result in more frequent and intense weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires. These extreme weather events can have devastating effects on ecosystems and the species that depend on them. For example, wildfires can destroy habitats and displace wildlife, while droughts can lead to water scarcity and loss of vegetation.
Another way in which climate change affects nature is through ocean acidification. As the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases, more of it is absorbed by the oceans, leading to a decrease in the pH of seawater. This makes it harder for marine organisms such as corals, mollusks, and plankton to build and maintain their shells and skeletons, which can have far-reaching impacts on the food web and marine ecosystems as a whole.
Climate change also affects biodiversity by altering the distribution and abundance of species. As temperatures change, some species may move to new areas, while others may become extinct. This can lead to changes in the composition of ecosystems and the relationships between species. For example, if a predator species moves to a new area, it may have a significant impact on the prey species in that area, leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Finally, climate change also affects the availability of resources such as food, water, and energy, which can have economic and social impacts on human societies. For example, changes in agricultural productivity due to climate change can lead to food shortages and higher food prices, while changes in water availability can affect water-dependent industries such as hydroelectric power generation and tourism.
In conclusion, climate change is having a profound impact on nature and the species that depend on it. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns are altering the timing and location of seasonal events, leading to mismatches between species and disruptions in ecosystems. Ocean acidification is making it harder for marine organisms to build and maintain their shells and skeletons, and changes in biodiversity are altering the composition of ecosystems and the relationships between species. The availability of resources is also being affected, which can have economic and social impacts on human societies. It is crucial that we take immediate action to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the natural world for future generations. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting and restoring ecosystems, and supporting sustainable resource management practices. By doing so, we can help ensure that the planet remains a healthy and vibrant place for all species to thrive.