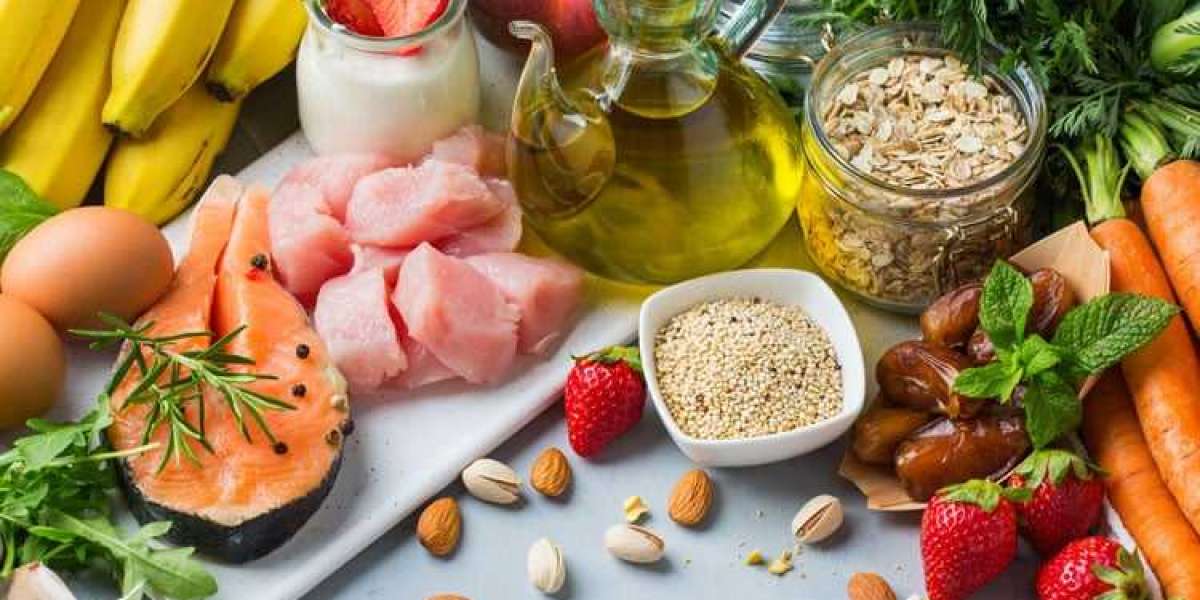
Special diets are diets that are designed to address specific health concerns or conditions. Here are some examples of special diets:
Gluten-free diet: This diet is recommended for individuals with celiac disease, a condition where the body cannot tolerate gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Low-carb diet: This diet is commonly used for weight loss and involves reducing the intake of carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and sugar.
Ketogenic diet: This is a low-carb, high-fat diet that can help with weight loss and also has therapeutic benefits for certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy and type 2 diabetes.
Vegan diet: A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. It is typically followed for ethical, environmental, or health reasons.
Paleo diet: This diet is based on the presumed diet of ancient humans and emphasizes whole foods such as meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, while avoiding processed foods, grains, and dairy products.
It is important to note that special diets should only be followed under the guidance of a healthcare professional and should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment.