Congestive Heart Failure Disease Overview:
Congestive Heart Failure Disease (CHF) is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This article delves into the intricacies of CHF, covering its classification, stages, signs and symptoms, diagnostic analysis, treatment options, regulatory framework, clinical trials, market insights, epidemiology, and emerging trends in the field.
Additionally, research published in the JACC Journal Organization indicates that heart failure (HF) significantly increases the morbidity and mortality associated with cardiovascular disease. It is estimated that 6.2 million adults in the US have HF, and between 2012 and 2030, that figure is expected to increase by 46% to reach >8 million persons under the age of 18. Apart from the medical consequences of heart failure, the estimated yearly financial burden is $30.7 billion in the United States.
Classification of CHF:
Congestive Heart Failure can be classified into two primary categories based on the ejection fraction, a measure of the heart's pumping ability:
- Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF): This occurs when the left ventricle of the heart is weakened and can't pump blood effectively. The ejection fraction in HFrEF is typically less than 40%.
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF): In this type, the left ventricle is stiff, and although it can pump blood, it does so less efficiently. The ejection fraction in HFpEF is usually equal to or greater than 50%.
Congestive Heart Failure Disease Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
Imaging Tests:
· General Electric Company (GE Healthcare)
· TECHNOMANCY
· Siemens Healthineers
· Med Imaging Solutions
· Canon Medical Systems Corporation
· Gastro diagnostic.Ltd
· Radiance Imaging system
· Philips Healthcare
· Allengers Medical System Ltd.
Tissue Sampling:
· Roche Diagnostics
· Becton, Dickinson, and Company (BD)
· Abbott Laboratories
· Hologic, Inc.
Browse In-depth Research Report on Congestive Heart Failure Disease:
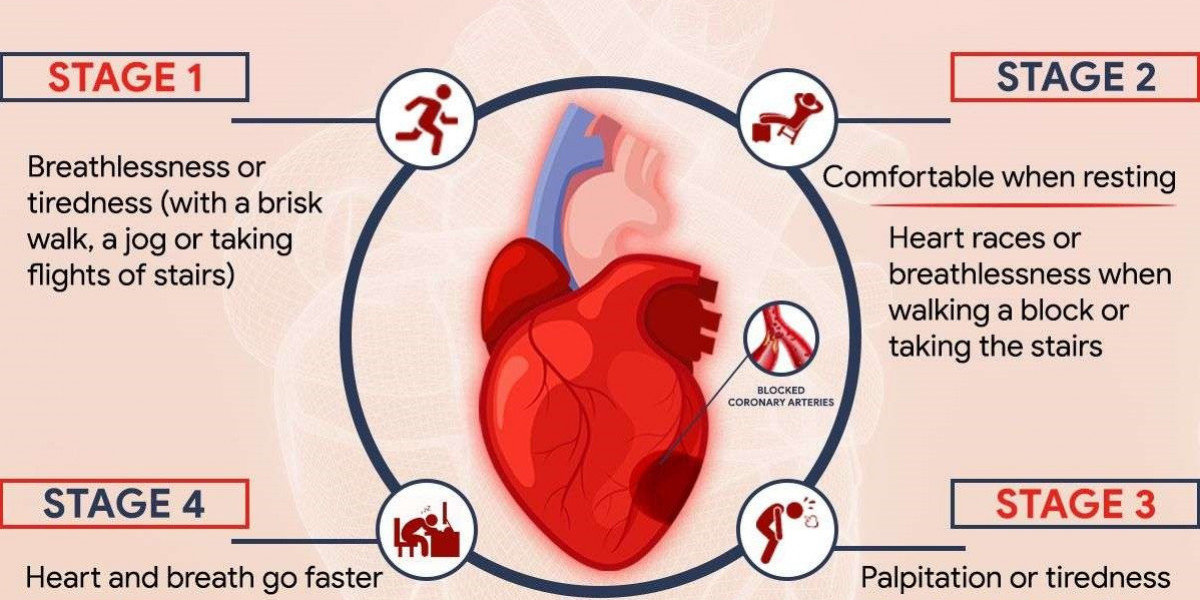
Stages of Heart Failure:
CHF is typically categorized into four stages:
- Stage I (High Risk): At this stage, the patient is at risk of developing heart failure but shows no symptoms or structural heart damage.
- Stage II (Mild): There may be minor symptoms like shortness of breath during physical activity, but no limitation in daily activities.
- Stage III (Moderate): Patients in this stage experience significant limitations in physical activity due to symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Stage IV (Severe): This is the most advanced stage, where patients are unable to carry out any physical activity without discomfort, and symptoms may be present even at rest.
Signs & Symptoms:
Common signs and symptoms of CHF include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying down.
- Persistent cough or wheezing.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema).
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Reduced ability to exercise.
- Sudden weight gain.
Congestive Heart Failure Disease Diagnostic Analysis:
Diagnosing CHF typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as:
- Echocardiogram: A critical imaging tool that can assess the heart's structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures electrical activity of the heart.
- Chest X-ray: Can reveal heart and lung abnormalities.
- Blood tests: To check for specific markers of heart failure.
- Cardiac catheterization: Measures pressure in the heart's chambers and can help identify blockages in coronary arteries.
Congestive Heart Failure Disease Treatment Analysis:
Treatment for CHF aims to relieve symptoms, improve the patient's quality of life, and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and more.
- Lifestyle changes: Dietary modifications, exercise programs, and weight management.
- Cardiac devices: Implantable devices like pacemakers and defibrillators.
- Surgery: Heart transplantation or ventricular assist devices for severe cases.
Regulatory Framework for Congestive Heart Failure Disease:
The regulatory landscape for CHF treatments is stringent, with various national and international health agencies overseeing drug and device approvals. Clinical trials and rigorous testing are mandatory for any new treatment to ensure safety and efficacy.
Clinical Trial Assessment:
Numerous clinical trials are ongoing to develop innovative treatments and therapies for CHF. These trials focus on novel drug formulations, advanced medical devices, and cutting-edge surgical techniques.
Price and Market Access:
The market for CHF treatments is substantial, driven by the increasing prevalence of the disease. The cost of CHF treatment varies depending on the stage and severity of the condition, with more advanced stages often requiring more expensive interventions. Ensuring access to these treatments remains a global healthcare challenge.
Epidemiology Study:
CHF is a global health concern. It affects people of all ages, although the risk increases with age. Several epidemiological studies are ongoing to better understand the prevalence and incidence of CHF in different populations.
Market Trends:
As healthcare technology advances, there is a growing focus on precision medicine and personalized treatments for CHF. Telemedicine and remote monitoring are emerging as key trends, allowing patients to manage their condition more effectively while reducing hospitalizations.
Surgical and Other Procedures:
In advanced cases, surgical interventions like heart transplantation or the implantation of ventricular assist devices may be necessary. These procedures aim to replace or support a failing heart, improving the patient's quality of life.
Conclusion:
Congestive Heart Failure is a complex medical condition that requires a multi-faceted approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. As research and innovation in the field continue to evolve, we can expect to see more effective treatments and a deeper understanding of this disease, providing hope to millions of CHF patients worldwide.
Browse Through More Cardiovascular Diseases Research Reports:
For More Related Reports:
Unlocking the Most Recent Advances in Alzheimer's Disease research: a glimmer of hope
Global Insights on Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) Disease: Rising Against the Odds
Understanding Crohn's Disease: Its Causes, Signs, and Treatment
Demystifying Parkinson's Disease: A Closer Look at its Complex Nature
Cardiomyopathy Disease Research Trends and Clinical Trials