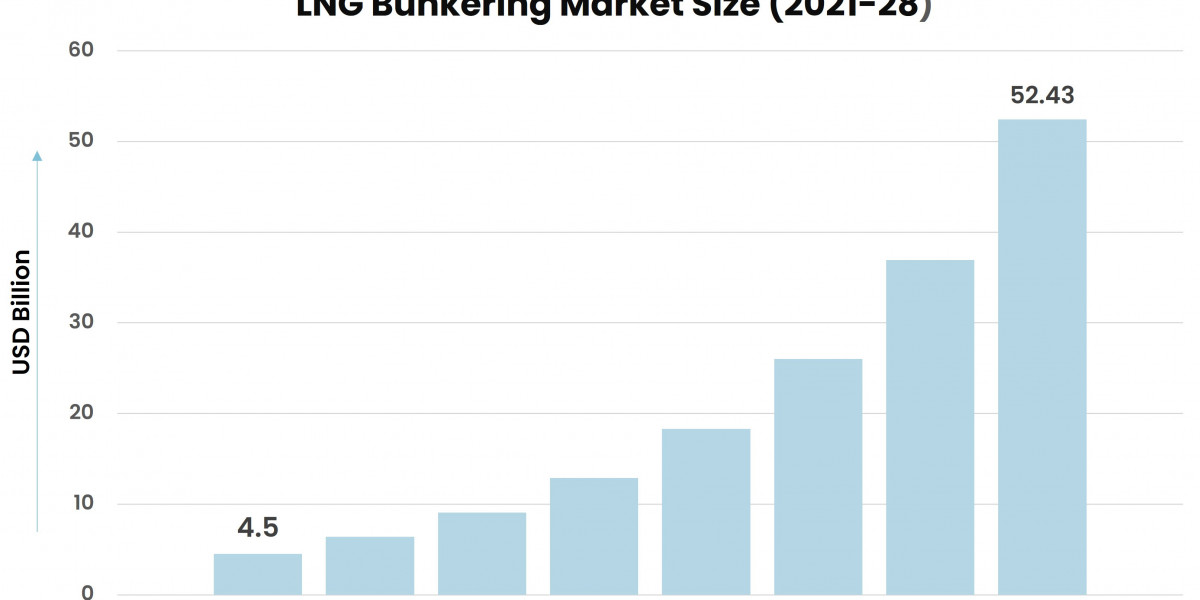
According to Stratview Research, the LNG bunkering market was estimated at USD 4.5 billion in 2021 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 42% during 2022-2028 to reach USD 52.43 billion in 2028.
As the world grapples with the urgency of climate change, industries are seeking cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions. In the maritime sector, liquefied natural gas (LNG) has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional marine fuels, offering reduced emissions and improved environmental performance. This article delves into the LNG bunkering market, examining its growth trajectory, key drivers, and implications for the future of maritime transportation.
The Rise of LNG Bunkering
LNG bunkering involves the transfer of liquefied natural gas from storage facilities to ships for use as fuel. With stricter emissions regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainability, LNG has gained traction as a viable option for powering ships, particularly in areas where emissions standards are stringent, such as Emission Control Areas (ECAs) and ports.
The past decade has witnessed a significant increase in LNG bunkering infrastructure development, driven by a combination of regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and market demand. LNG bunkering vessels, terminals, and fueling stations are being established worldwide to support the adoption of LNG as a marine fuel.
Environmental Benefits
One of the primary drivers behind the adoption of LNG bunkering is its environmental advantages over conventional marine fuels. LNG emits lower levels of sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter compared to heavy fuel oil (HFO) and marine diesel oil (MDO). Additionally, LNG combustion results in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, making it a cleaner alternative in terms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
By transitioning to LNG as a marine fuel, shipowners and operators can achieve compliance with stringent emissions regulations while contributing to overall environmental sustainability goals. As the global focus on decarbonization intensifies, LNG bunkering is positioned to play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of the maritime industry.
Market Dynamics and Growth Prospects
The LNG bunkering market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by a confluence of factors including regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and shifting market dynamics. The International Maritime Organization's (IMO) sulfur cap regulations, which limit the sulfur content of marine fuels, have accelerated the adoption of LNG as a compliant alternative.
Moreover, advancements in LNG bunkering infrastructure, including the development of ship-to-ship (STS) transfer systems and bunkering vessels, have bolstered confidence in LNG as a feasible marine fuel option. As a result, shipowners and operators are increasingly investing in LNG-powered vessels and retrofitting existing fleets to accommodate LNG propulsion systems.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the LNG bunkering market presents promising opportunities for the maritime industry, it also faces challenges that must be addressed to ensure its sustainable growth. Infrastructure development, including the establishment of LNG bunkering hubs and supply chains, remains a key challenge, particularly in regions with limited LNG infrastructure.
Additionally, concerns related to safety, regulatory compliance, and investment costs pose barriers to widespread adoption. However, concerted efforts by industry stakeholders, governments, and regulatory bodies to address these challenges are paving the way for the expansion of the LNG bunkering market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the LNG bunkering market represents a paradigm shift in the maritime industry's approach to fueling vessels. As the world seeks cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions, LNG emerges as a frontrunner, offering significant environmental benefits and compliance with stringent emissions regulations. With continued investment in infrastructure, technological innovation, and regulatory support, LNG bunkering is poised to fuel the future of maritime transportation, driving forward the industry's transition towards a greener and more sustainable future.